Multicloud has become the de facto IT infrastructure model in organizations across the world over the past two or three years – Flexera’s State of the Cloud 2022 report found that 9 out of 10 SMBs and enterprises now operate in a multicloud environment.
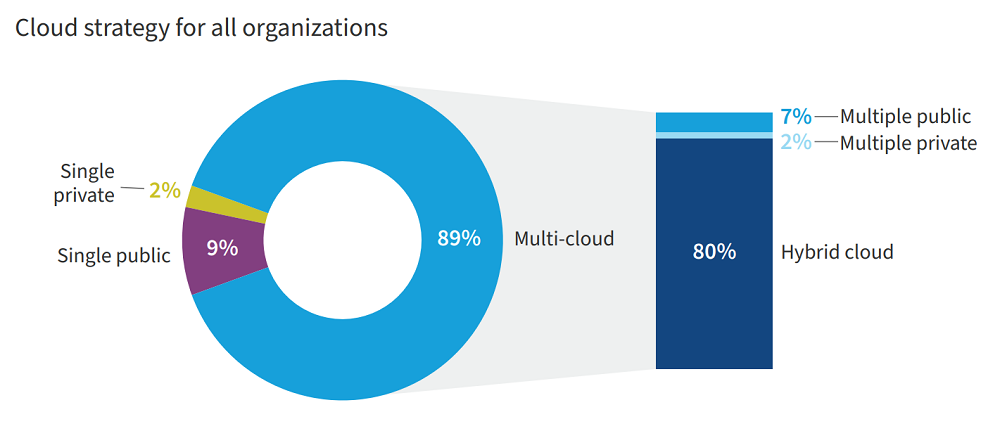
Source: Flexera
Further, multicloud is the only operating model with an upward adoption trajectory, according to the 4th annual Nutanix Enterprise Cloud Index report. While the pandemic changed working habits and practices almost overnight, organizations that had a multicloud deployment in place (or could set one up quickly) were ready with the infrastructure to deal with it.
“COVID-19 has accelerated the migration to cloud computing,” said Jim Ryan, CEO of Flexera. “Still, cloud isn’t magic or the land of milk and honey. Companies are moving fast, facing challenges, and trying to connect cloud computing to business outcomes.”
Multicloud has some obvious long-term business benefits for enterprises. That’s why organizations are implementing multicloud strategies to run mission-critical workloads and applications.
“Most organizations adopt a multicloud strategy out of a desire to avoid vendor lock-in or to take advantage of best-of-breed solutions,” said Michael Warrilow, Research VP Analyst, Gartner. “We expect that most large organizations will continue to willfully pursue this approach.”
Of course, individual apps rarely span multiple clouds. The most common multicloud implementation involves apps siloed on different clouds while DR & failover come a close second.
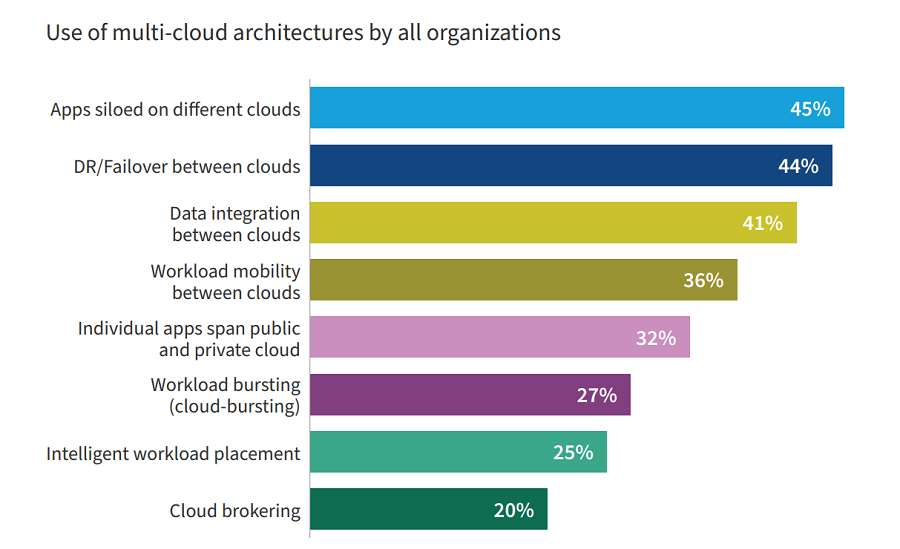
Source: Flexera
Enterprises in different industries can deploy a multicloud architectures by examining a few use cases.
1. Digital Transformation and Cloud Adoption
With most companies looking to embrace AI, ML, IoT, and other emerging technologies as they arrive, they are thinking strategically about where to run their workloads. They are looking for a dynamic IT infrastructure that scales and in doing so, moving away from an all-or-nothing cloud vs. data center approach to a cloud-smart approach. They want to match their workloads to the right cloud environments based on speed, security, cost, flexibility, and other factors.
“We are on a path of IT transformation, to really embrace cloud technologies, artificial intelligence and machine learning, not only for our customers but also internally,” said Dr. Nandish Mattikalli, Chief Engineer for Intelligence Solutions at BAE Systems, a legendary defense contractor that makes weapons systems and combat vehicles for land, sea and air. They were able to implement Agile and DevOps methodologies, speed up their development cycle, and achieve continuous integration / continuous delivery (CI/CD) as a result of deploying a hybrid, multicloud architecture.
Multicloud technologies make a big difference when it comes to development speed and security with flexibility. Nutanix Frame, a DaaS technology, enabled shorter development cycles at BAE by skipping several development activities, said Dr. Mattikalli. “Defense agencies want rapid development and deployment of minimal viable products. They also want constant updates and security patches, just as iPhone buyers expect Apple to keep their devices secure,” he explained.
2. Data Management, Storage and Analytics
Leveraging and managing data in the cloud is a core function that drives most businesses forward today. Be it sales, product development or customer services, enterprises need to analyze and use data efficiently to empower their customers and employees as well as speed up business transformation.
At the moment, enterprise data could be scattered across many locations – on-premise data centers, stand-alone servers, employees’ laptops or phones, edge devices or various clouds in a multicloud environment itself.
As enterprises pick and choose cloud systems from multiple vendors – based on performance and leverage – they also need better tools to manage data and enable automation and AI across these systems.
“Enterprise applications and data need to be portable across varying public cloud environments, and also be interoperable with on-premises private clouds,” said Krista Macomber, Sr. Analyst, Data Protection and Multi-Cloud Data Management, at Evaluator Group.
A multicloud initiative lies at the core of the world’s largest brewer Anheuser Busch InBev’s global data strategy “We knew we had to do so much at such a rapid pace. We couldn't afford to be on premises and wait months and years to do things,” said Harinder Singh, their Global Director of Enterprise Data Management & Governance at the time.
Backup and archiving is a common multicloud use case in the enterprise. Specialized cloud storage services provide low-cost and safe backup options while enabling fast and efficient data transfer on-demand. The pay-as-you-go terms allow for scalability and longer retention periods while reducing CAPEX while off-site data replication facilities reduce OPEX.
“Thanks to user-friendly cloud interfaces, moving data across clouds and making multiple copies of data sets in one click results in the reduced investments in development resources,” said Andrei Lipnitski, IT Director at ScienceSoft, an IT consulting company based in Texas.
When it comes to analytics, multicloud is important not just for enterprises, but even cloud vendors themselves, who are working hard to extend their capabilities and performance in multicloud environments – Infoweek reported that data integration vendor Talend reinvented itself as a cloud data integration and data integrity company to take advantage of opportunities in the multicloud market.
3. Application Portability between Data Centers and Cloud Systems
Many organizations still have mission-critical applications that they can’t really decide where to run – on a private cloud or a public cloud, or even on a cloud or a data center. They need the capability to move data and apps from on-prem data centers to the cloud and back again without spending millions or turning it into a huge project for half their IT team.
Multicloud environments can lend this flexibility to enterprise applications by
- Accelerating the migration with compression and change block tracking
- Simplifying data transfer between heterogeneous systems or clouds
- Offering tools for control, management and compatibility across public and private clouds from different vendors
- Providing reliability and security of data, services and applications across the environment
Multicloud helps make on and off-ramping data and applications simple, flexible and cost-effective with a hybrid IT infrastructure strategy.
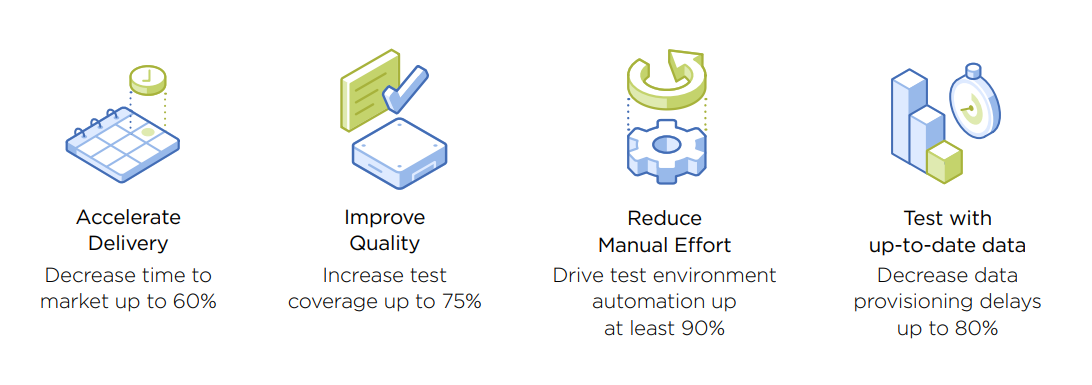
This has clear benefits in software development, testing and DevOps. Enterprises have always found setting up and managing DevTest ecosystems to be time and resource-intensive. “DevTest is the biggest pain point because current tooling is not efficient across the data center and cloud environments. So testing is slow and problematic,” said Anish Behanan, Sr. Director & Practice Leader at Capgemini.
Nutanix and Capgemini saw an opportunity to offer solutions in application delivery, Agile and DevTest development in distributed architectures via a partnership.
“We saw the value in bringing solutions to market together that solve specific use cases. In the past, we’ve often asked customers to knit together components of solutions. But that isn’t fast enough for some companies, especially with the amount of testing going on in many industries, especially financial services and insurance,” said Tapan Mehta, former head of industry strategy and solutions at Nutanix. “The most agile companies are in a race to retool and re-platform so they can build new apps and services and revise legacy ones quickly.”
Eventually, Nutanix and Capgemini collaborated with value stream management platform vendor Plutora to create Smart Foundry, a holistic private and public multicloud Test Environment Management (TEM) platform that integrates with existing development tools, data management functions and development pipeline.
Source: Nutanix
Smart Foundry delivers multi-premise, cloud-agnostic and industry-specific testing solutions for deploying cloud apps. It incorporates cutting-edge technologies and practices such as multicloud provisioning, virtualization, container management, interactive configuration management databases, chaos engineering, observability and auto-healing.
“Smart Foundry provides DevTest teams everything they need to operate in almost any kind of cloud environment,” said Behanan. “It helps teams test applications thoroughly to make sure they’re truly ready to be deployed.”
Multicloud gives developers the resources they need to create data sets and clones for building, testing and deploying apps into production within an affordable OPEX model. It leverages the inherent accessibility and portability of the cloud, which extends to all file servers, applications, services and databases needed for development.
4. Risk Mitigation and Disaster Recovery
Along with giving organizations a wider choice of service offerings and SLAs, multicloud increases the resilience of these services. Spreading data and apps across two or more providers reduces the organization’s exposure to service outages and lowers the risk of disruption to operations.
“Having data in different locations, especially in terms of primary and secondary data, means that the customer doesn’t have all his eggs in one basket,” said Charles Foley, Sr. Director at NetApp.
Data can be abstracted away from cloud apps and stored in a shared pool accessible from anywhere in the multicloud environment. This reduces data duplication, prevents data fragmentation and improves data governance.
Just like data abstraction and virtualization, clustering also helps in risk mitigation. Clustering typically applies to data sets – if something goes wrong with databases that contain sensitive data, the results could be catastrophic for the organization. Since clustering needs two compute instances, it can’t be implemented with block storage in a single cloud. Multicloud overcomes this limitation and provides redundancy in such cases.
Of course, disaster recovery is one of the obvious and most common use cases of multicloud. Off-site cloud-based DR has grown increasingly practical and cost-efficient over the years.
Bringing Down Complexity with Strategy
Enterprises are dealing with challenges in security, cloud spend, and lack of skilled personnel in managing multicloud environments. Understanding cloud computing trends is key to selecting the best cloud vendors and MSPs for each business function, speeding up decision-making, and estimating TCO of the cloud infrastructure.
Ad hoc addition of cloud services without an integrated approach or a holistic cloud strategy is doomed to fail, according to Kapil Makhija, Head of Technology Cloud and Business Development at Oracle.
“Multicloud should be a deliberate and cohesive strategy,” he said. “It’s similar to the practice of choosing many different software providers on-premises to avoid lock-in and then assembling best-of-breed solutions in one’s own data center, but via a cloud-model that delivers increased agility and superior cloud economics.”
Featured image: Pxfuel
Dipti Parmar is a marketing consultant and contributing writer to Nutanix. She’s a columnist for major tech and business publications such as IDG’s CIO.com, Adobe’s CMO.com, Entrepreneur Mag, and Inc. Follow Dipti on Twitter @dipTparmar or connect with her on LinkedIn for little specks of gold-dust-insights.
© 2022 Nutanix, Inc. All rights reserved. For additional legal information, please go here.